Cloud Workspace Setup
If you plan to use this repository with the Openscapes 2i2c JupyterHub Cloud Workspace there are no additional setup requirements for the Python environment. All packages needed are included unless specified within a notebook, in which case a cell will be dedicated to installing the necessary Python libraries using the appropriate package manager.
After completing the prerequisites you will have access to the Openscapes 2i2c JupyterHub cloud workspace. Click here to start JupyterLab. Use your email and the provided password to sign in. This password will be provided in the workshop. If you’re interested in using the 2i2c cloud workspace outside of the workshop, please contact us.
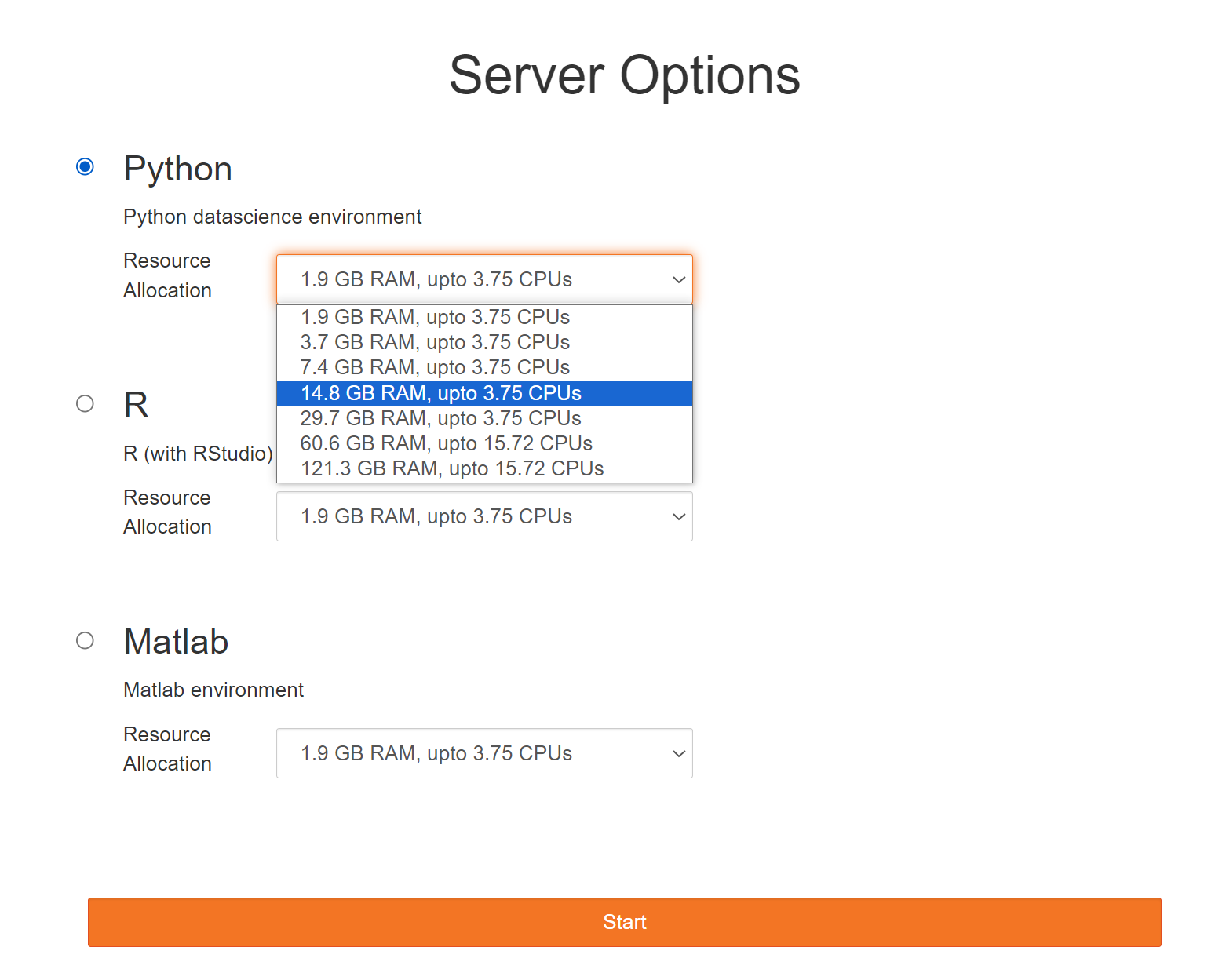
After signing in you will be prompted for some server options:
Select the following options:
- Environment: Other…
- Custom image: openscapes/python:d8e6ca2
- Resource Allocation: ~15 GB RAM and ~1.8 CPUs
Cloning the NEON and NASA repositories
Once the cloud workspace with the required Python environment is spun up, you can clone the repositories containing the NEON and NASA notebooks as follows.
NEON Notebooks
To clone the repository containing the NEON notebooks, navigate to the directory where you want to store the repository on Openscapes (your home directory), then type the following from the terminal or command prompt:
git clone https://github.com/NEONScience/neon-nasa-hsi-workshop.gitTo locate and start running the NEON notebooks, change directories (cd) to neon-nasa-hsi-workshop/neon
cd neon-nasa-hsi-workshop/neonNASA Notebooks
To clone the repository containing the NASA airborne notebooks, navigate to the directory where you want to store the repository on Openscapes (your home directory)
cd ~Then type the following from the terminal or command prompt:
git clone https://github.com/ornldaac/airborne.gitTo find and open the NASA notebooks, change directories to where the airborne notebooks are saved:
cd airborne/notebooksTroubleshooting
We recommend Shutting down all kernels after running each notebook. This will clear the memory used by the previous notebook, and is necessary to run some of the more memory intensive notebooks.
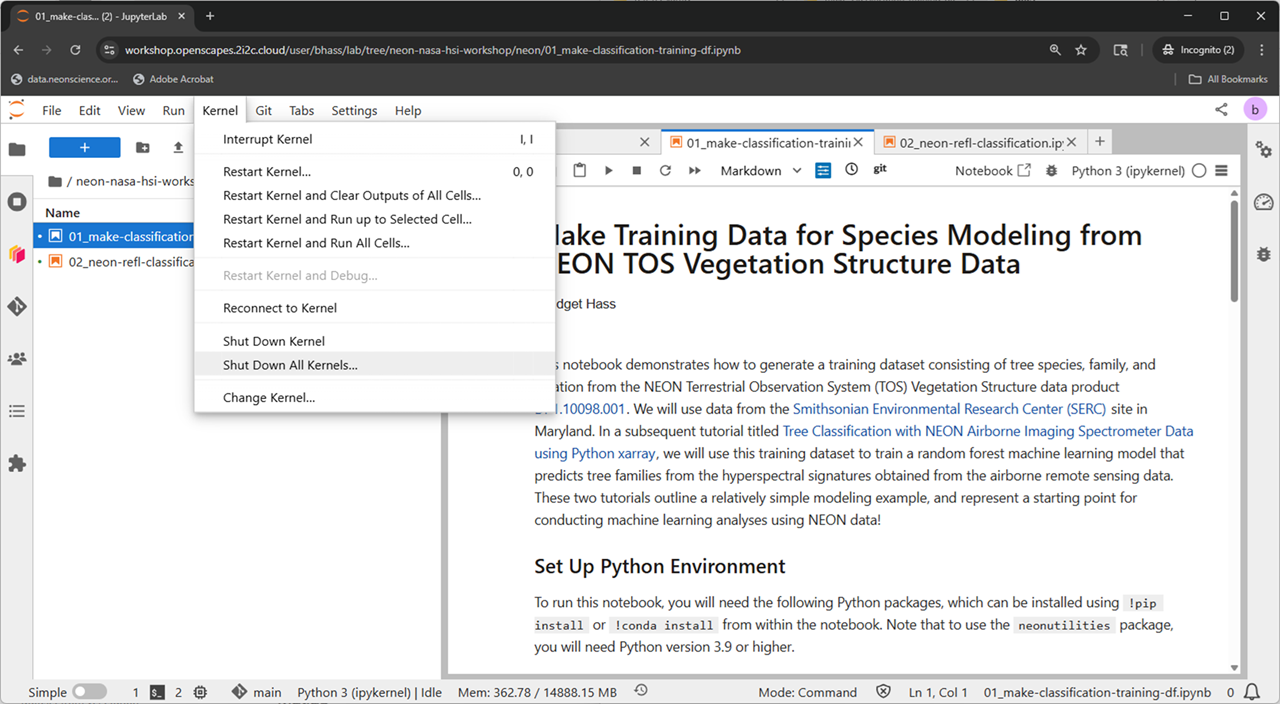
No single notebook exceeds roughly the limit using the provided data, but if you choose to use your own data in the notebook, or have 2 notebooks open and do not shut down the kernel, you may get an out of memory error.
Tricks to avoid potential pitfalls
The notebooks in this workshop use relative paths and assume you are working from the same working directory as the instructors. If you are not finding a data file in the right path, we recommend the following troubleshooting steps to make sure you are in the right place.
- To show your current working directory in Python, type into a notebook cell:
import os
os.getcwd() # get current working directory- To display the contents (files, folders) in you current directory, use
!ls.lsis a Linux command meaning list directory. You can run linux commands from a code cell directly when you add an exclamation mark (!) in front of the command.
!ls # list contents of current directory- You can also install Python packages in this way (using
!), for example:
!pip install neonutilities # install the neonutilities Python packageContributing
If you plan to edit or contribute to this NEON NASA Airborne Hyperspectral Workshop Repository repository, or the NEON-Data-Skills repository, we recommend following a fork and pull workflow: first fork the repository, then clone your fork to your local machine, make changes, push changes to your fork, then make a pull request back to the main repository.
